Next: Metric
Up: No Title
Previous: Median
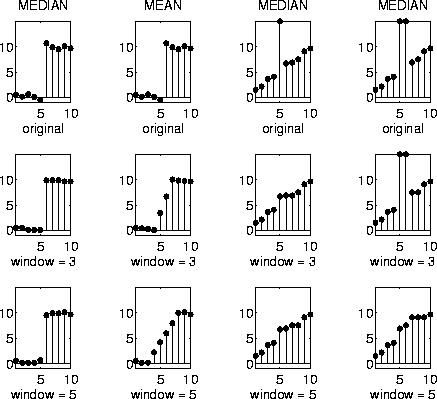
Median filtering is a non-linear signal enhancement technique
(  Image Enhancement)
for the smoothing of signals, the suppression of impulse noise,
and preserving of edges.
In the one-dimensional case it consists of sliding a window of an odd
number of elements along the signal,
replacing the centre sample by the median of the samples in the window.
In the following picture we use window sizes of 3 and 5 samples. The
first two columns show a step function, degraded by some random noise.
The two last columns show a noisy straight line, and in addition one
and two samples, which are considerably different from the neighbour
samples.
Image Enhancement)
for the smoothing of signals, the suppression of impulse noise,
and preserving of edges.
In the one-dimensional case it consists of sliding a window of an odd
number of elements along the signal,
replacing the centre sample by the median of the samples in the window.
In the following picture we use window sizes of 3 and 5 samples. The
first two columns show a step function, degraded by some random noise.
The two last columns show a noisy straight line, and in addition one
and two samples, which are considerably different from the neighbour
samples.
Whereas the median filter in the first column preserves the edge
very well, the low-pass filtering method in the second column smoothes
the edge completely. Columns 3 and 4 show the importance of the window
size: one sample out of range can be easily removed with a window size
of 3, whereas two neighbouring samples can only be removed with a
larger window.
For more details, see [Pratt78].
Rudolf K. Bock, 7 April 1998