This tutorial assumes the reader knows:
(1) How to develop source code to read BMP header and info header
(i.e. width, height & # of colors).
(2) How to develop source code to read raster data
This tutorial will teach you how to:
(1) Detect edges using the Sobel method.
(2) Detect edges using the Laplace method.
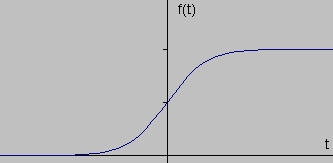
Edges characterize boundaries and are therefore a problem of fundamental importance in image processing. Edges in images are areas with strong intensity contrasts – a jump in intensity from one pixel to the next. Edge detecting an image significantly reduces the amount of data and filters out useless information, while preserving the important structural properties in an image. There are many ways to perform edge detection. However, the majority of different methods may be grouped into two categories, gradient and Laplacian. The gradient method detects the edges by looking for the maximum and minimum in the first derivative of the image. The Laplacian method searches for zero crossings in the second derivative of the image to find edges. An edge has the one-dimensional shape of a ramp and calculating the derivative of the image can highlight its location. Suppose we have the following signal, with an edge shown by the jump in intensity below:

If we take the gradient of this signal (which, in one dimension, is just the first derivative with respect to t) we get the following:
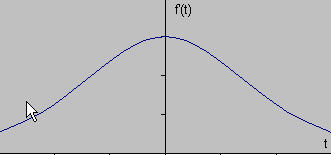
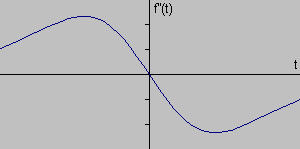
Clearly, the derivative shows a maximum located at the center of the edge in the original signal. This method of locating an edge is characteristic of the “gradient filter” family of edge detection filters and includes the Sobel method. A pixel location is declared an edge location if the value of the gradient exceeds some threshold. As mentioned before, edges will have higher pixel intensity values than those surrounding it. So once a threshold is set, you can compare the gradient value to the threshold value and detect an edge whenever the threshold is exceeded. Furthermore, when the first derivative is at a maximum, the second derivative is zero. As a result, another alternative to finding the location of an edge is to locate the zeros in the second derivative. This method is known as the Laplacian and the second derivative of the signal is shown below:
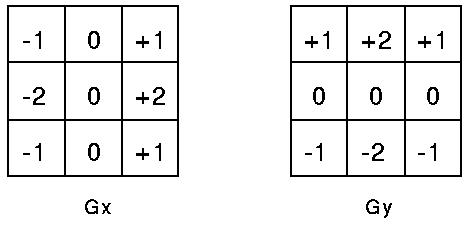
Based on this one-dimensional analysis, the theory can be carried over to two-dimensions as long as there is an accurate approximation to calculate the derivative of a two-dimensional image. The Sobel operator performs a 2-D spatial gradient measurement on an image. Typically it is used to find the approximate absolute gradient magnitude at each point in an input grayscale image. The Sobel edge detector uses a pair of 3x3 convolution masks, one estimating the gradient in the x-direction (columns) and the other estimating the gradient in the y-direction (rows). A convolution mask is usually much smaller than the actual image. As a result, the mask is slid over the image, manipulating a square of pixels at a time. The actual Sobel masks are shown below:
The magnitude of the gradient is then calculated using the formula:

An approximate magnitude can be calculated using:
The code for the Sobel edge detector is shown below and uses the above gradient approximation.
/*
FILE: edgeSob.c - WORKS!!
AUTH: Bill Green
DESC: 2 3x3 Sobel masks for edge detection
DATE: 07/23/02
REFS: edgeLap.c
*/
#include (stdio.h)
#include (stdlib.h)
#include (math.h)
#include (alloc.h)
/*-------STRUCTURES---------*/
typedef struct {int rows; int cols; unsigned char* data;} sImage;
/*-------PROTOTYPES---------*/
long getImageInfo(FILE*, long, int);
void copyImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile);
void copyColorTable(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile, int nColors);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
FILE *bmpInput, *bmpOutput;
sImage originalImage;
sImage edgeImage;
unsigned int X, Y;
int I, J;
long sumX, sumY;
int nColors, SUM;
unsigned long vectorSize;
unsigned long fileSize;
int GX[3][3];
int GY[3][3];
unsigned char *pChar, someChar;
unsigned int row, col;
someChar = '0'; pChar = &someChar;
/* 3x3 GX Sobel mask. Ref: www.cee.hw.ac.uk/hipr/html/sobel.html */
GX[0][0] = -1; GX[0][1] = 0; GX[0][2] = 1;
GX[1][0] = -2; GX[1][1] = 0; GX[1][2] = 2;
GX[2][0] = -1; GX[2][1] = 0; GX[2][2] = 1;
/* 3x3 GY Sobel mask. Ref: www.cee.hw.ac.uk/hipr/html/sobel.html */
GY[0][0] = 1; GY[0][1] = 2; GY[0][2] = 1;
GY[1][0] = 0; GY[1][1] = 0; GY[1][2] = 0;
GY[2][0] = -1; GY[2][1] = -2; GY[2][2] = -1;
if(argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: %s bmpInput.bmp\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
};
printf("Reading filename %s\n", argv[1]);
/*-------DECLARE INPUT & OUTPUT FILES-------*/
bmpInput = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
bmpOutput = fopen("edgeSob.bmp", "wb");
/*---SET POINTER TO BEGINNING OF FILE----*/
fseek(bmpInput, 0L, SEEK_END);
/*-------GET INPUT BMP DATA--------*/
fileSize = getImageInfo(bmpInput, 2, 4);
originalImage.cols = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 18, 4);
originalImage.rows = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 22, 4);
edgeImage.rows = originalImage.rows;
edgeImage.cols = originalImage.cols;
/*--------PRINT DATA TO SCREEN----------*/
printf("Width: %d\n", originalImage.cols);
printf("Height: %d\n", originalImage.rows);
printf("File size: %lu\n", fileSize);
nColors = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 46, 4);
printf("nColors: %d\n", nColors);
/*------ALLOCATE MEMORY FOR FILES--------*/
vectorSize = fileSize - (14+40+4*nColors);
printf("vectorSize: %lu\n", vectorSize);
edgeImage.data = farmalloc(vectorSize*sizeof(unsigned char));
if(edgeImage.data == NULL) {
printf("Failed to malloc edgeImage.data\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("%lu bytes malloc'ed for edgeImage.data\n", vectorSize);
originalImage.data = farmalloc(vectorSize*sizeof(unsigned char));
if(originalImage.data == NULL) {
printf("Failed to malloc originalImage.data\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("%lu bytes malloc'ed for originalImage.datt\n", vectorSize);
/*------COPY HEADER AND COLOR TABLE---------*/
copyImageInfo(bmpInput, bmpOutput);
copyColorTable(bmpInput, bmpOutput, nColors);
fseek(bmpInput, (14+40+4*nColors), SEEK_SET);
fseek(bmpOutput, (14+40+4*nColors), SEEK_SET);
/* Read input.bmp and store it's raster data into originalImage.data */
for(row=0; row<=originalImage.rows-1; row++) {
for(col=0; col<=originalImage.cols-1; col++) {
fread(pChar, sizeof(char), 1, bmpInput);
*(originalImage.data + row*originalImage.cols + col) = *pChar;
}
}
/*---------------------------------------------------
SOBEL ALGORITHM STARTS HERE
---------------------------------------------------*/
for(Y=0; Y<=(originalImage.rows-1); Y++) {
for(X=0; X<=(originalImage.cols-1); X++) {
sumX = 0;
sumY = 0;
/* image boundaries */
if(Y==0 || Y==originalImage.rows-1)
SUM = 0;
else if(X==0 || X==originalImage.cols-1)
SUM = 0;
/* Convolution starts here */
else {
/*-------X GRADIENT APPROXIMATION------*/
for(I=-1; I<=1; I++) {
for(J=-1; J<=1; J++) {
sumX = sumX + (int)( (*(originalImage.data + X + I +
(Y + J)*originalImage.cols)) * GX[I+1][J+1]);
}
}
/*-------Y GRADIENT APPROXIMATION-------*/
for(I=-1; I<=1; I++) {
for(J=-1; J<=1; J++) {
sumY = sumY + (int)( (*(originalImage.data + X + I +
(Y + J)*originalImage.cols)) * GY[I+1][J+1]);
}
}
/*---GRADIENT MAGNITUDE APPROXIMATION (Myler p.218)----*/
SUM = abs(sumX) + abs(sumY);
}
if(SUM>255) SUM=255;
if(SUM<0) SUM=0;
*(edgeImage.data + X + Y*originalImage.cols) = 255 - (unsigned char)(SUM);
fwrite((edgeImage.data + X + Y*originalImage.cols),sizeof(char),1,bmpOutput);
}
}
printf("See edgeSob.bmp for results\n");
fclose(bmpInput);
fclose(bmpOutput);
farfree(edgeImage.data); /* Finished with edgeImage.data */
farfree(originalImage.data); /* Finished with originalImage.data */
return 0;
}
/*----------GET IMAGE INFO SUBPROGRAM--------------*/
long getImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, long offset, int numberOfChars)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
long value = 0L;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, offset, SEEK_SET);
for(i=1; i<=numberOfChars; i++)
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
/* calculate value based on adding bytes */
value = (long)(value + (*ptrC)*(pow(256, (i-1))));
}
return(value);
} /* end of getImageInfo */
/*-------------COPIES HEADER AND INFO HEADER----------------*/
void copyImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, 0L, SEEK_SET);
fseek(outputFile, 0L, SEEK_SET);
for(i=0; i<=50; i++)
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
fwrite(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, outputFile);
}
}
/*----------------COPIES COLOR TABLE-----------------------------*/
void copyColorTable(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile, int nColors)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, 54L, SEEK_SET);
fseek(outputFile, 54L, SEEK_SET);
for(i=0; i<=(4*nColors); i++) /* there are (4*nColors) bytesin color table */
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
fwrite(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, outputFile);
}
}
The mask is slid over an area of the input image, changes that pixel's value and then shifts one pixel to the right and continues to the right until it reaches the end of a row. It then starts at the beginning of the next row. The example below shows the mask being slid over the top left portion of the input image represented by the green outline. The formula shows how a particular pixel in the output image would be calculated. The center of the mask is placed over the pixel you are manipulating in the image. And the I & J values are used to move the file pointer so you can mulitply, for example, pixel (a22) by the corresponding mask value (m22). It is important to notice that pixels in the first and last rows, as well as the first and last columns cannot be manipulated by a 3x3 mask. This is because when placing the center of the mask over a pixel in the first row (for example), the mask will be outside the image boundaries.
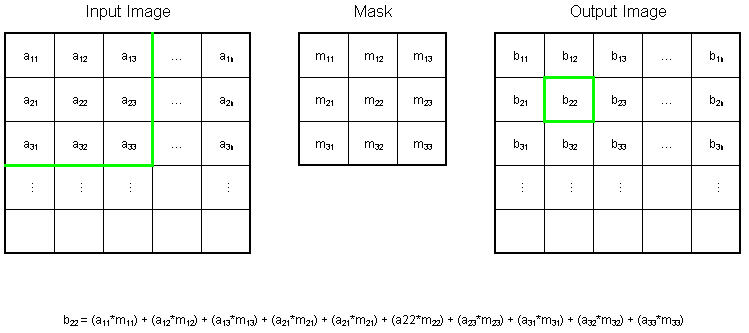
The GX mask highlights the edges in the horizontal direction while the GY mask highlights the edges in the vertical direction. After taking the magnitude of both, the resulting output detects edges in both directions.
The 5x5 Laplacian used is a convoluted mask to approximate the second derivative, unlike the Sobel method which approximates the gradient. And instead of 2 3x3 Sobel masks, one for the x and y direction, Laplace uses 1 5x5 mask for the 2nd derivative in both the x and y directions. However, because these masks are approximating a second derivative measurement on the image, they are very sensitive to noise, as can be seen by comparing edgeSob.bmp to edgeLap.bmp. The Laplace mask and code are shown below:
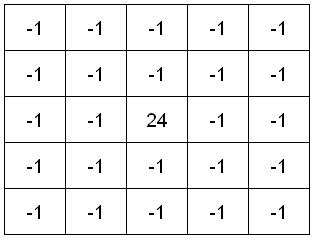
/*
FILE: edgeLap.c - WORKS!
AUTH: P.Oh
DESC: 5x5 Laplace mask for edge detection
DATE: 05/02/02 23:30
REFS: edgedeta.c
*/
#include (stdio.h)
#include (stdlib.h)
#include (math.h)
#include (alloc.h)
/*-------STRUCTURES---------*/
typedef struct {int rows; int cols; unsigned char* data;} sImage;
/*-------PROTOTYPES---------*/
long getImageInfo(FILE*, long, int);
void copyImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile);
void copyColorTable(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile, int nColors);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
FILE *bmpInput, *bmpOutput;
sImage originalImage;
sImage edgeImage;
unsigned int X, Y;
int I, J;
long SUM;
int nColors;
unsigned long vectorSize;
unsigned long fileSize;
int MASK[5][5];
unsigned char *pChar, someChar;
unsigned int row, col;
someChar = '0'; pChar = &someChar;
/* 5x5 Laplace mask. Ref: Myler Handbook p. 135 */
MASK[0][0] = -1; MASK[0][1] = -1; MASK[0][2] = -1; MASK[0][3] = -1; MASK[0][4] = -1;
MASK[1][0] = -1; MASK[1][1] = -1; MASK[1][2] = -1; MASK[1][3] = -1; MASK[1][4] = -1;
MASK[2][0] = -1; MASK[2][1] = -1; MASK[2][2] = 24; MASK[2][3] = -1; MASK[2][4] = -1;
MASK[3][0] = -1; MASK[3][1] = -1; MASK[3][2] = -1; MASK[3][3] = -1; MASK[3][4] = -1;
MASK[4][0] = -1; MASK[4][1] = -1; MASK[4][2] = -1; MASK[4][3] = -1; MASK[4][4] = -1;
if(argc < 2) {
printf("Usage: %s bmpInput.bmp\n", argv[0]);
exit(0);
};
printf("Reading filename %s\n", argv[1]);
/* open files for reading and writing to */
bmpInput = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
bmpOutput = fopen("edgeLap.bmp", "wb");
/* start pointer at beginning of file */
fseek(bmpInput, 0L, SEEK_END);
/* retrieve and print filesize and number of cols and rows */
fileSize = getImageInfo(bmpInput, 2, 4);
originalImage.cols = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 18, 4);
originalImage.rows = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 22, 4);
edgeImage.rows = originalImage.rows;
edgeImage.cols = originalImage.cols;
printf("Width: %d\n", originalImage.cols);
printf("Height: %d\n", originalImage.rows);
printf("File size: %lu\n", fileSize);
/* retrieve and print Number of colors */
nColors = (int)getImageInfo(bmpInput, 46, 4);
printf("nColors: %d\n", nColors);
vectorSize = fileSize - (14+40+4*nColors);
printf("vectorSize: %lu\n", vectorSize);
edgeImage.data = farmalloc(vectorSize*sizeof(unsigned char));
if(edgeImage.data == NULL) {
printf("Failed to malloc edgeImage.data\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("%lu bytes malloc'ed for edgeImage.data\n", vectorSize);
originalImage.data = farmalloc(vectorSize*sizeof(unsigned char));
if(originalImage.data == NULL) {
printf("Failed to malloc originalImage.data\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("%lu bytes malloc'ed for originalImage.datt\n", vectorSize);
copyImageInfo(bmpInput, bmpOutput);
copyColorTable(bmpInput, bmpOutput, nColors);
fseek(bmpInput, (14+40+4*nColors), SEEK_SET);
fseek(bmpOutput, (14+40+4*nColors), SEEK_SET);
/* Read input.bmp and store it's raster data into originalImage.data */
for(row=0; row<=originalImage.rows-1; row++) {
for(col=0; col<=originalImage.cols-1; col++) {
fread(pChar, sizeof(char), 1, bmpInput);
*(originalImage.data + row*originalImage.cols + col) = *pChar;
}
}
for(Y=0; Y<=(originalImage.rows-1); Y++) {
for(X=0; X<=(originalImage.cols-1); X++) {
SUM = 0;
/* image boundaries */
if(Y==0 || Y==1 || Y==originalImage.rows-2 || Y==originalImage.rows-1)
SUM = 0;
else if(X==0 || X==1 || X==originalImage.cols-2 || X==originalImage.cols-1)
SUM = 0;
/* Convolution starts here */
else {
for(I=-2; I<=2; I++) {
for(J=-2; J<=2; J++) {
SUM = SUM + (int)( (*(originalImage.data + X + I +
(Y + J)*originalImage.cols)) * MASK[I+2][J+2]);
}
}
}
if(SUM>255) SUM=255;
if(SUM<0) SUM=0;
*(edgeImage.data + X + Y*originalImage.cols) = 255 - (unsigned char)(SUM);
fwrite((edgeImage.data + X + Y*originalImage.cols),sizeof(char),1,bmpOutput);
}
}
printf("See edgeLap.bmp for results\n");
fclose(bmpInput);
fclose(bmpOutput);
farfree(edgeImage.data); /* Finished with edgeImage.data */
farfree(originalImage.data); /* Finished with originalImage.data */
return 0;
}
/*----------GET IMAGE INFO SUBPROGRAM--------------*/
long getImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, long offset, int numberOfChars)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
long value = 0L;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, offset, SEEK_SET);
for(i=1; i<=numberOfChars; i++)
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
/* calculate value based on adding bytes */
value = (long)(value + (*ptrC)*(pow(256, (i-1))));
}
return(value);
} /* end of getImageInfo */
/*-------------COPIES HEADER AND INFO HEADER----------------*/
void copyImageInfo(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, 0L, SEEK_SET);
fseek(outputFile, 0L, SEEK_SET);
for(i=0; i<=50; i++)
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
fwrite(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, outputFile);
}
}
/*----------------COPIES COLOR TABLE-----------------------------*/
void copyColorTable(FILE* inputFile, FILE* outputFile, int nColors)
{
unsigned char *ptrC;
unsigned char dummy;
int i;
dummy = '0';
ptrC = &dummy;
fseek(inputFile, 54L, SEEK_SET);
fseek(outputFile, 54L, SEEK_SET);
for(i=0; i<=(4*nColors); i++) /* there are (4*nColors) bytesin color table */
{
fread(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, inputFile);
fwrite(ptrC, sizeof(char), 1, outputFile);
}
}
The Laplace algorithm works the exact same way as the Sobel, except a little simpler because it only uses one mask instead of two.